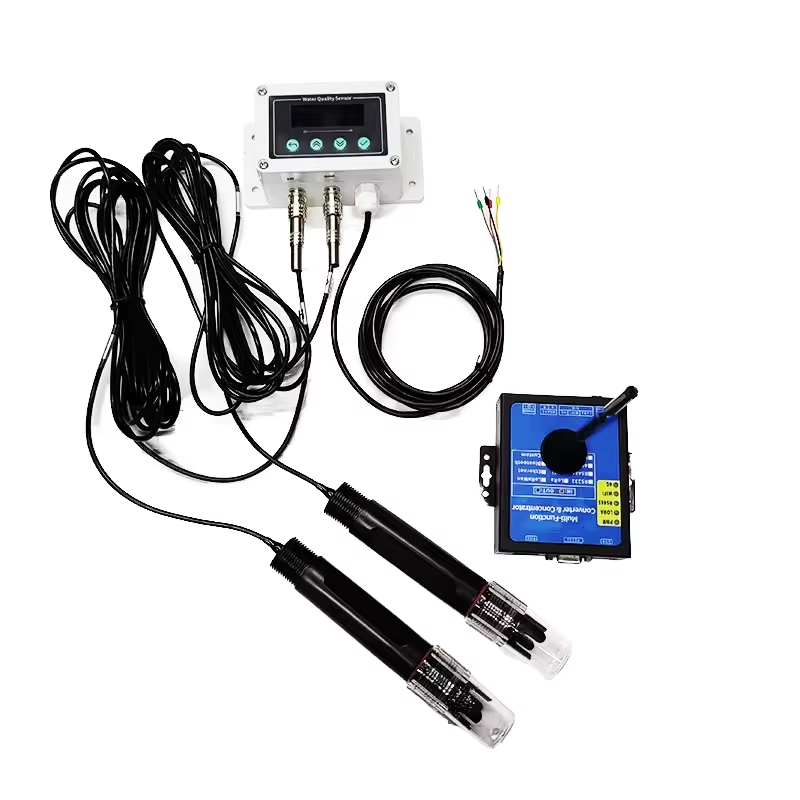
Lima, Peru — In a significant leap forward for agricultural practices in Peru, the introduction of pH and oxidation-reduction potential (ORP) water quality sensors equipped with screens is transforming how farmers monitor and manage their irrigation systems. As the agricultural sector faces the dual challenges of climate change and water scarcity, these advanced sensors are becoming essential tools that enhance crop yield, improve resource efficiency, and promote sustainable farming practices.
The Need for Innovation in Peruvian Agriculture
Peru’s agriculture is diverse, ranging from highland crops like potatoes and quinoa to coastal produce such as avocados and grapes. However, this vital sector is highly susceptible to fluctuations in water availability and quality, which are exacerbated by climate change and environmental degradation. Farmers have increasingly turned to technology to address these challenges, seeking more efficient ways to optimize their water use and ensure healthier crops.
How pH and ORP Sensors Work
The newly deployed water quality sensors measure critical parameters such as pH levels and ORP, providing real-time data on water quality directly via built-in screens. pH is a vital indicator of soil health, affecting nutrient availability and microbial activity. ORP, on the other hand, helps determine the oxidative state of the water, which can influence the health of both plants and aquatic ecosystems.
By utilizing these sensors, farmers can make informed decisions about irrigation practices, ensuring that their crops receive the optimal conditions for growth.
Transformative Impact on Agricultural Practices
-
Enhanced Crop Yields:
Access to real-time data allows farmers to adjust irrigation practices based on the specific needs of their crops. For instance, understanding soil pH helps farmers determine the right time to apply fertilizers, enhancing nutrient uptake and, consequently, crop yields. Farmers in regions like Ica, known for its vineyards, are experiencing firsthand the benefits of maintaining optimal soil conditions, resulting in healthier and more productive plants. -
Water Conservation:
With many areas facing chronic water shortages, the precision offered by pH and ORP sensors enables farmers to use water more efficiently. By applying water only when necessary and in appropriate amounts, farmers can conserve this precious resource while still maintaining healthy crops. This approach is particularly crucial in arid regions of Peru, where water scarcity remains a pressing concern. -
Sustainable Farming Practices:
The integration of these sensors aligns with the growing trend towards sustainable agriculture. By minimizing chemical runoff and reducing the over-application of fertilizers, farmers contribute to soil health and ecosystem balance. This sustainable approach is particularly important as international markets increasingly demand environmentally friendly practices. -
Economic Benefits:
Improved yields and more efficient water use directly contribute to greater economic stability for farmers. With enhanced productivity, many smallholder farmers in regions like Cajamarca can increase their income and invest in better tools and methods, fostering rural development and strengthening community resilience.
Real-Life Applications and Success Stories
Farmers across Peru are already reporting success stories attributed to the use of pH and ORP sensors. In the coastal region of La Libertad, farmers cultivating asparagus are now able to fine-tune their irrigation practices, resulting in a 20% increase in yield. Similarly, avocado producers in the lush regions of Ucayali have noted improved fruit quality and size due to better-managed irrigation based on precise water quality data.
Future Prospects
The adoption of pH and ORP sensors is just one component of a larger trend towards precision agriculture in Peru. As the government and private sector continue to invest in agricultural technology, farmers are optimistic about the future. Enhanced education and training programs will be essential to ensure that producers can effectively utilize these tools and embrace modern farming practices.
In conclusion, the integration of pH and ORP water quality sensors is significantly impacting agriculture in Peru, driving innovation while addressing critical challenges in water management, crop production, and sustainability. As farmers adopt this technology, the potential for a more resilient agricultural sector is within reach, promising a prosperous future for Peru’s farming communities and ensuring food security in the face of global challenges.
For moreWater quality sensor information,
please contact Honde Technology Co., LTD.
Email: info@hondetech.com
Company website: www.hondetechco.com
Post time: Feb-12-2025