Abstract
Flow and sediment problem is one of the key factors which affect the dispatching operation and life of the Three Gorges Project (TGP). Many approaches have been employed to research the flow and sediment problems of the TGP during its demonstration, planning, design, construction and operation, and many important results have been obtained. To understand the progress of flow and sediment measurement in China’s representative projects and the experience of sediment observation in super large reservoirs, the flow and sediment measurement of the TGP is mainly introduced in this paper. It includes the general situation of the TGP, the distribution of the hydrological station network, the measurement factors, the new measurement technology, and the sediment changes in the reservoir and downstream after the impoundment of the TGP. The sediment measurement results show that the basic situation of sediment problems is good, and these sediment problems may probably accumulate, develop, and transform over time, so they should be paid continuous attention.
1 INTRODUCTION
The Three Gorges Project (TGP) is the largest water conservation and hydro-power project in the world. The dam is at Sandouping, Yichang City, Hubei Province, which is the dividing line between the mid-stream and upstream of the trunk stream of the Yangtze River. It controls a drainage area of 1 million km2, and the average annual runoff volume reaches 451,000 million m3. With a flood storage capacity of 22.15 billion cubic meters, the project plays a major role in the flood control of the Yangtze River basin. With a normal impounded level of 175 m, the total storage capacity of the reservoir is 39,300 and 22,150 million m3 of it is the flood control capacity. The development of the TGP focuses on flood-prevention, power generation, and water transportation benefits. It will also improve the ecological environment. Over that period, comprehensive benefits regarding flood control, navigation, power generation, and water resource utilization were delivered.
As a key part of the flood control system in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, the TGP controls 96% of the inflow to Jingjiang River, the most dangerous river section during floods, and over two-thirds of the inflow to Wuhan. The TGP plays an indispensable role in mitigating the floods and in reducing the massive floods in the upper reaches of the Yangtze River. By the end of August, the dam had held back 180 billion cubic meters of water during flood seasons. It saw inflows of over 70,000 cubic meters per second in 2010, 2012 and reduced flood peaks by about 40%, greatly easing flood-control pressure in downstream areas. During dry seasons, discharges have been raised to more than 5500 cubic meters per second, providing more than 20 billion cubic meters of water a year for the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River.
The prototype observation is executed to serve the sediment research, construction, and operation of the TGP in the different period. Prototype measurements were used to analyze the variations in runoff and sediment load in the main channel of the Yangtze River, as well as the changes and evolution of the riverbed. The distribution of sites is shown in Figure 1. The current observation results are basically consistent with the feasibility study stage (Lu & Huang, 2013), but due to the reduction of upstream sediment and the construction of cascade reservoirs on the Jinsha River after the 1990s, the sedimentation of the Three Gorges reservoir (TGR) is much smaller than before, resulting in a greater intensity and distance of riverbed erosion downstream of the TGP.
2 HYDROLOGIC NETWORK DESIGN AND MEASUREMENT SYSTEM
To collect basic data and to provide services for basin engineering construction, the Changjiang Water Resources Commission has gradually established a large number of hydrological stations along the main stream and tributaries of the Yangtze River since the 1950s. By the 1990s, a complete hydrological station network and sediment monitoring network had been basically formed. It includes 118 hydrological stations and more than 350 gauging stations . In addition, a large amount of river survey and sediment analysis work has been completed. The hydrological and sediment observation data of the past decades for several generations provided a scientific basis for the demonstration, design, construction, and operation of the TGP.
The prototype observation is executed to serve the sediment research, construction, and operation of the TGR in the different period. After the reservoir began its storage in 2003, the sediment issue appeared both in upper and lower reaches, and the prototype observation and corresponding sediment research were executed to serve operation of TGP directly . The observation goal includes the following aspects: Mastering the background data of natural channel status before impounding completely; Making reference for the decision of installment impounding plan; real-time monitoring of the variation of erosion and deposition both in upper and lower reaches after impounding, and finding out the problems, so as to take countermeasure in time; validating the simulation technology adopted, and increasing the credibility of TGP sediment forecasting.
The hydrological sediment prototype observation range includes the reservoir area, dam site, and lower reaches. Since 1949, based on long time’s sediment measure, channel observation, and exploration and investigation, lots of prototype observation data and analysis research results had been accumulated, thus meet the demand of planning, design and scientific research in definition phase. The construction phase is an interim to succeed the prophase, and the total period of construction is 17a, so it necessary to continuously observe the variation runoff, sediment, and boundary condition. This not only provides dependence for design, scientific research, construction, and operation, but also for validation and optimization of design and regulation.
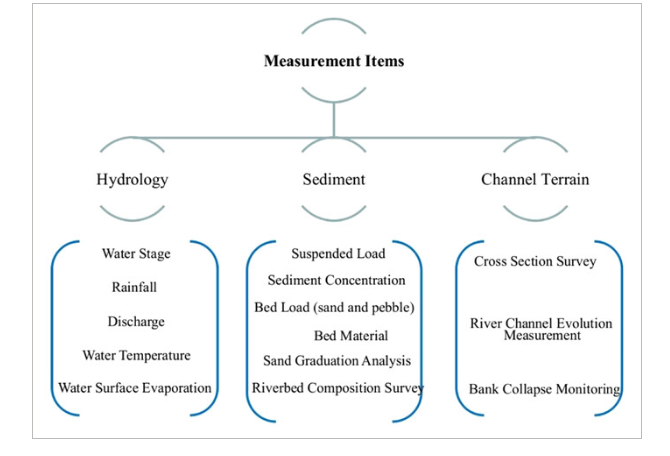
The monitoring factors mainly include hydrology, sediment, and channel terrain . The channel terrain survey is mainly to get the regularity of evolution of channel in the raw, the sediment deposition at the reservoir, erosion downstream, and evolution of the key reaches after the impoundment of the TGP.
2 HYDROLOGIC NETWORK DESIGN AND MEASUREMENT SYSTEM
To collect basic data and to provide services for basin engineering construction, the Changjiang Water Resources Commission has gradually established a large number of hydrological stations along the main stream and tributaries of the Yangtze River since the 1950s. By the 1990s, a complete hydrological station network and sediment monitoring network had been basically formed. It includes 118 hydrological stations and more than 350 gauging stations . In addition, a large amount of river survey and sediment analysis work has been completed. The hydrological and sediment observation data of the past decades for several generations provided a scientific basis for the demonstration, design, construction, and operation of the TGP.
The prototype observation is executed to serve the sediment research, construction, and operation of the TGR in the different period. After the reservoir began its storage in 2003, the sediment issue appeared both in upper and lower reaches, and the prototype observation and corresponding sediment research were executed to serve operation of TGP directly . The observation goal includes the following aspects: Mastering the background data of natural channel status before impounding completely; Making reference for the decision of installment impounding plan; real-time monitoring of the variation of erosion and deposition both in upper and lower reaches after impounding, and finding out the problems, so as to take countermeasure in time; validating the simulation technology adopted, and increasing the credibility of TGP sediment forecasting.
The hydrological sediment prototype observation range includes the reservoir area, dam site, and lower reaches. Since 1949, based on long time’s sediment measure, channel observation, and exploration and investigation, lots of prototype observation data and analysis research results had been accumulated, thus meet the demand of planning, design and scientific research in definition phase. The construction phase is an interim to succeed the prophase, and the total period of construction is 17a, so it necessary to continuously observe the variation runoff, sediment, and boundary condition. This not only provides dependence for design, scientific research, construction, and operation, but also for validation and optimization of design and regulation.
The monitoring factors mainly include hydrology, sediment, and channel terrain . The channel terrain survey is mainly to get the regularity of evolution of channel in the raw, the sediment deposition at the reservoir, erosion downstream, and evolution of the key reaches after the impoundment of the TGP.
Radar water level flow speed sensor for scenarios such as DAMS, open channels, and underground pipe networks, it can monitor data in real time
Post time: Nov-04-2024